BT. Shunt
BT. Shunt
BT. Shunt
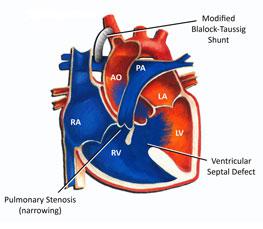
Blalock-Taussig (BT) Shunt
A Blalock-Taussig (BT) shunt is a small tube that connects the arterial circulation to the pulmonary circulation in order to get more blood to the lungs. This is the first in a series of operations required to correct complex congenital (present at birth) heart defects. A BT shunt is a temporary fix, as it is only a certain size, but it allows the baby to grow to better prepare for his or her next operation.
Symptoms
• Rapid heartbeat.
• Rapid breathing.
• Swelling of the legs, tummy or around the eyes.
• Extreme tiredness and fatigue.
• A blue tinge to the skin or lips (cyanosis)
• Tiredness and rapid breathing when a baby is feeding.
Diagnosis
• Echocardiogram
• Electrocardiogram (ECG)
• Chest x-ray
During Surgery
The Blalock-Taussig (BT) shunt mimics the role of the ductus arteriosus, meaning it allows blood to flow from a major artery through a connection to the pulmonary artery. Not only does this allow more blood to be oxygenated by the lungs, it also encourages the pulmonary arteries to grow, making the next surgery easier.
A BT shunt is tiny, measuring less than 5 millimeters (0.20 inches) in diameter. A surgeon attaches the two ends of the shunt to a major blood vessel, such as the subclavian artery, and to the pulmonary artery. The high-pressure arterial system will force blood through the BT shunt to the lungs to pick up more oxygen. The shunt helps to return healthy color to a child whose skin, lips or fingernails may have appeared blue (cyanosis) because of low oxygen levels in the blood. But even with a BT shunt, children likely will not have normal oxygen saturation levels and can appear blue, or cyanotic. The child’s oxygen saturation levels after a BT shunt will depend on the type of heart defect that is being repaired.
Complications after surgery
• Bleeding, clotting, strokes
• Shunt blockage
• Tube infection
• Excessive blood flow to the lungs risking vessel damage or decreased flow of blood to the brain and body
Duration: 4-5 hours
Success Rate: 95-97% may vary according to patient’s condition.
Stay in Hospital: 08-10 days
Stay in India: 20-25 days